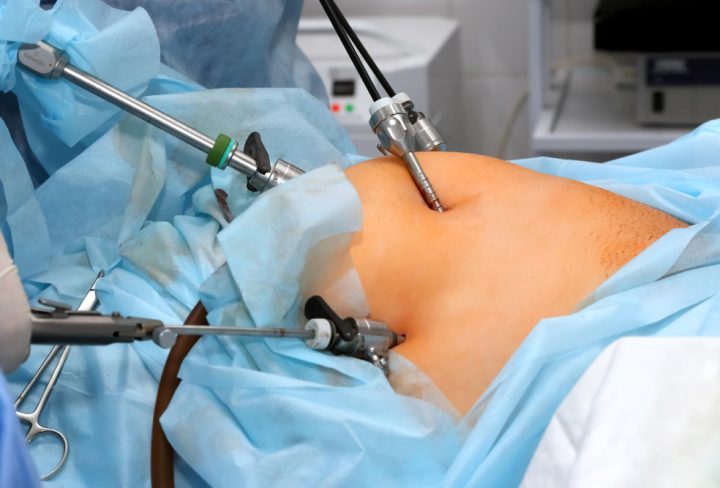
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a modern surgery that fixes hernias using small cuts and a camera. This method is important because it often leads to less pain and a quicker recovery. Many people choose laparoscopic hernia repair for its gentle approach and smaller scars. If you or a loved one has a hernia, understanding this procedure can help you make informed choices.
What Is Laparoscopic Hernia Repair?
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive surgery. Instead of one large cut, the surgeon makes a few small cuts. Through these, a thin tube with a camera (called a laparoscope) and special tools are used. This lets the surgeon see inside and fix the hernia. In contrast, open surgery uses a bigger cut and takes longer to heal. Because of this, many people prefer the laparoscopic method for hernia repair.
Common Symptoms and Causes of Hernias
Hernias happen when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the muscle. You may notice a bulge or swelling in your belly or groin. But, not all hernias cause pain right away. Still, it is important to know the signs and causes.
Common causes include:
How Is Laparoscopic Hernia Repair Performed?
During laparoscopic hernia repair, the surgeon follows several careful steps. Here is a simple overview:
Most people go home the same day or the next.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernia repair offers many advantages over open surgery. Because of the smaller cuts, you may notice:
For these reasons, many patients and doctors prefer this approach.
Risks and Possible Complications
Like any surgery, laparoscopic hernia repair has some risks. However, most problems are rare and can be managed. Possible risks include:
Your surgeon will discuss these risks and explain how they are handled. If you notice severe pain, fever, or redness, contact your doctor right away.
Recovery and Aftercare Tips
After laparoscopic hernia repair, most people recover quickly. Still, following your doctor’s advice helps you heal faster. Here are some helpful tips:
Most people return to work or school within one to two weeks. However, always check with your surgeon before resuming full activity.
Prevention and Lifestyle Guidance
While not all hernias can be prevented, you can lower your risk. Try these tips to keep your belly muscles strong:
By making these changes, you can help protect your body and lower your chances of a hernia.
Frequently Asked Questions
When to Consult a Surgeon
If you notice a new lump, pain, or swelling in your belly or groin, see a doctor soon. Also, if you have sudden pain, vomiting, or the bulge cannot be pushed back, seek help right away. Early treatment can prevent serious problems. Never ignore warning signs or delay care.
References
Consult a specialist for personalized guidance on laparoscopic hernia repair.